Photoaging: How To Prevent Sun-Damaged Skin
What is Photoaging? Explore causes and prevention techniques to challenge photoaging for healthier-looking skin.
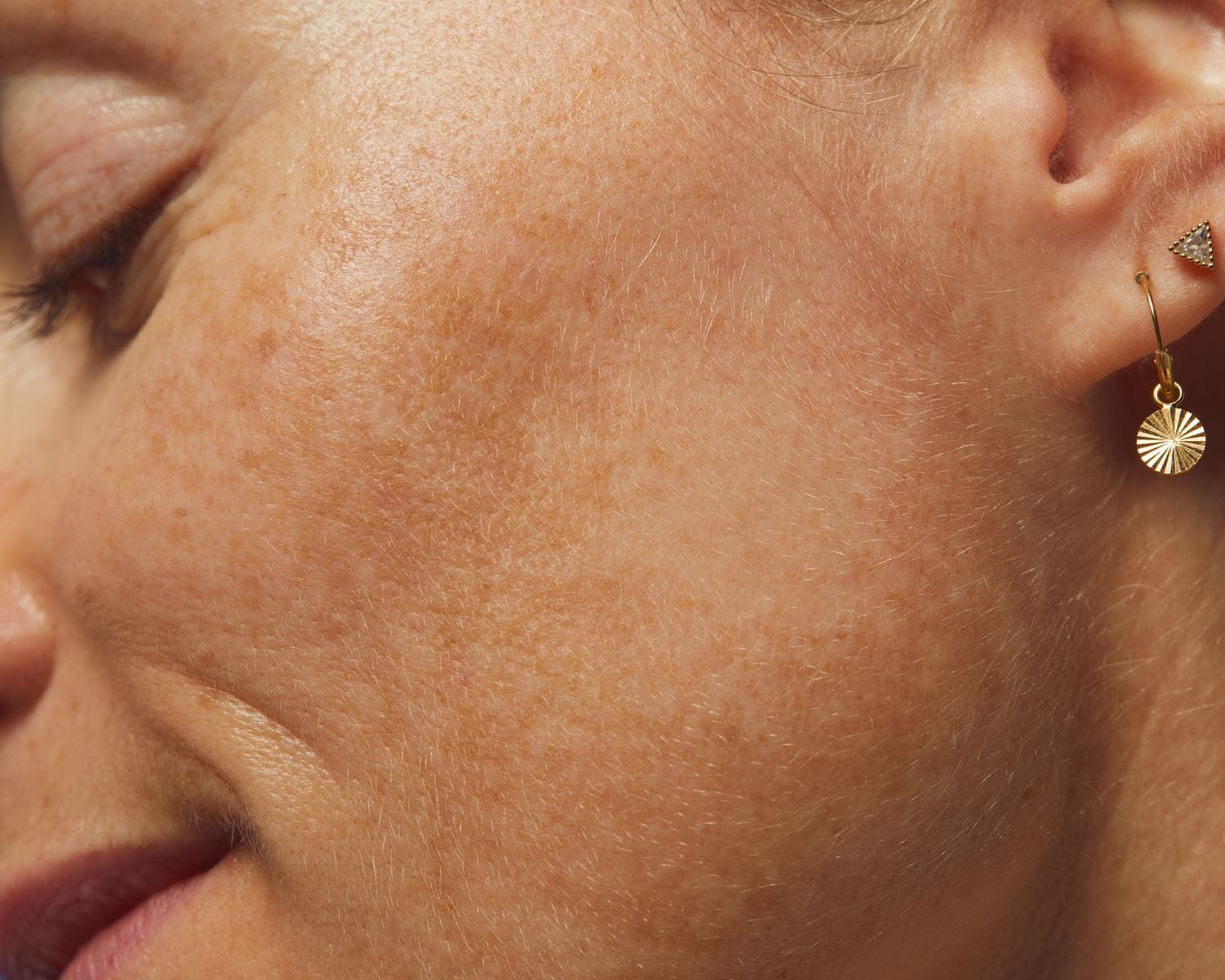
What is photoaging?
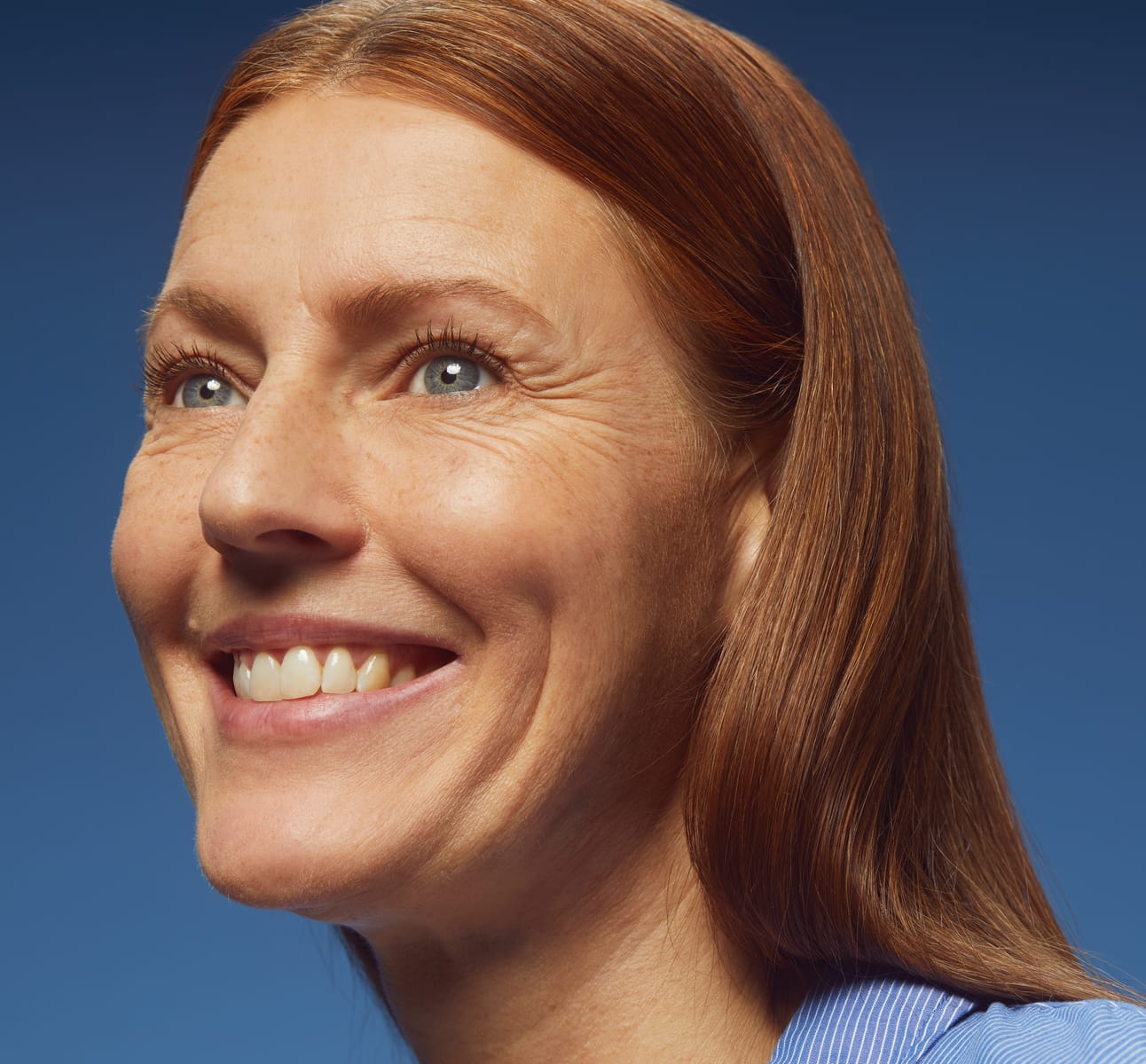
Photoaging is a form of premature ageing as a result of sun damage on the skin. It manifests as a range of visible signs, including sun wrinkles, fine lines, pigmentation irregularities, and loss of elasticity. While the sun's UV rays play a major role, high-energy visible (HEV) light can also induce oxidative stress, harming cellular DNA. Ensuring year-round protection and utilising high-quality sun care products are essential for prevention.
IS THERE A DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PHOTOAGING AND SUN DAMAGE?
Sun damage is a broad term that encompasses any negative effect that UV radiation has on the skin. This notably includes sunburn, hyperpigmentation, sun sensitivity reactions, damages to DNA, as well as premature ageing. Photoaging is a specific type of sun damage that refers to the premature ageing of the skin as a consequence of chronic exposure to UV radiation.
Time is the key difference between the two - sun damage generally refers to the immediate effects of UV radiation, whilst photoaging is a gradual process that can take years to become noticeable.
Time is the key difference between the two - sun damage generally refers to the immediate effects of UV radiation, whilst photoaging is a gradual process that can take years to become noticeable.
What Causes Photoaging
5 Causes of Photoaging
Addressing sun-induced skin damage is crucial not only for cosmetic reasons but also for overall skin health. Sun exposure is a leading cause of various skin concerns, such as photoaging and skin cancer, making it essential to understand and mitigate its effects.
THE EFFECTS OF THE SUN ON THE SKIN
Facts Overview
Photoaging
NIVEA Skin Routine For Sun Damaged Skin
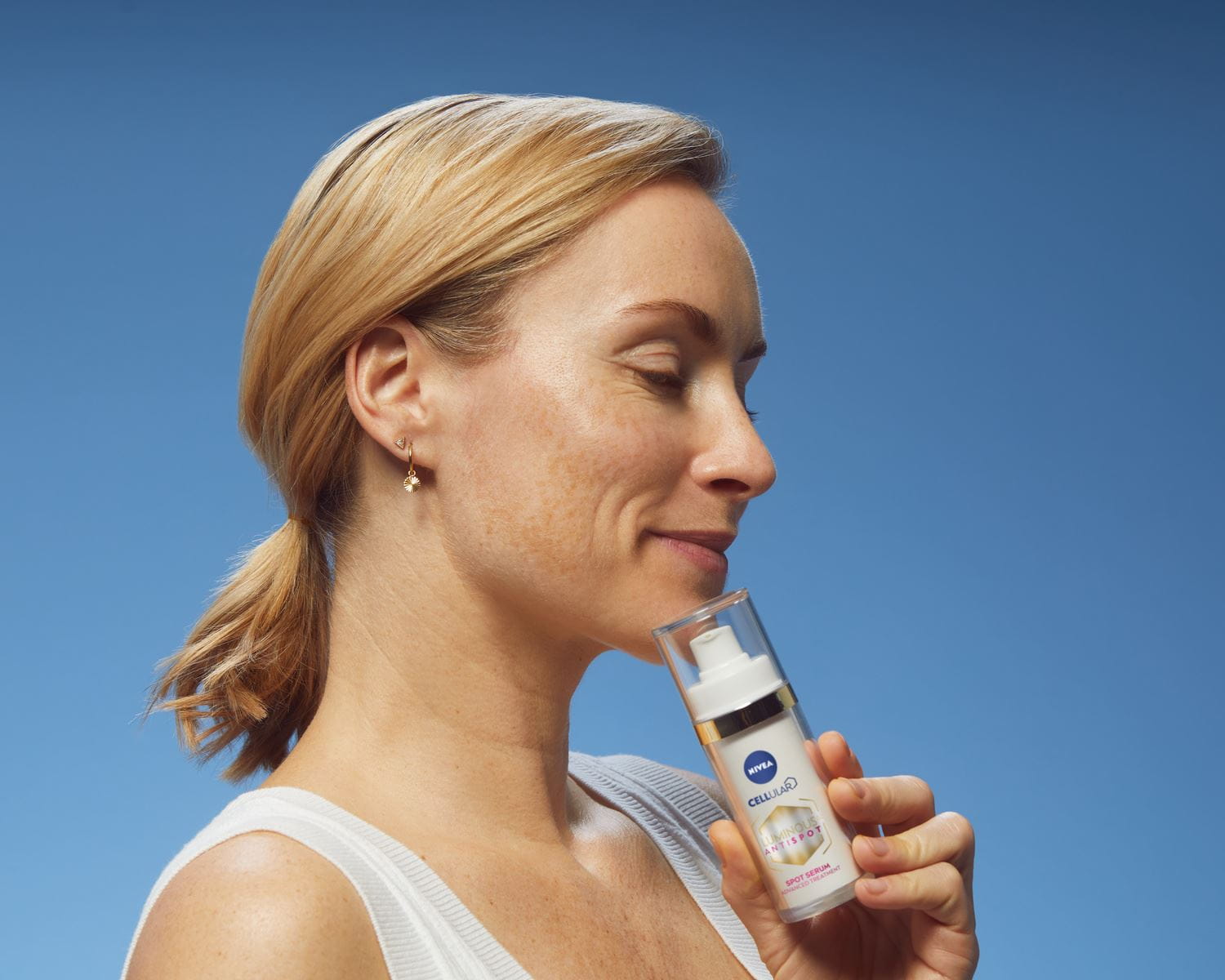
Minimise Signs of Photoaging with Q10 and Luminous630® Ranges
NIVEA Q10 Power Anti-Wrinkle Skincare Routine
The NIVEA Q10 Power range contains products formulated to address fine lines and wrinkles, giving you noticeably firmer skin in 14 days*. The NIVEA Q10 Power products combine 100% Skin Identical Q10 and Creatine to improve skin's elasticity and firmness.
NIVEA Luminous630® Anti-Dark Spot Skincare Routine
NIVEA’s Luminous630® range of products has been carefully created to provide targeted action against dark spots. The patented Thiamidol ingredient works at a cellular level to balance melanin production and reduce the appearance of dark spots.
Use Sunscreen Daily to Help Prevent Signs of Photoaging
Additional Ways to Minimise the Risks of Sun Damage
Summary
It's important to note that everyone is susceptible to some degree of photoaging, and preventive measures, such as sun protection, a healthy lifestyle, and proper skincare, can help mitigate its effects. Regularly using a broad-spectrum sunscreen, seeking shade, and wearing protective clothing are essential in preventing and minimising photoaging.